When Chi Xu left Magic Leap and returned to China, he had big ambitions. He believed China would have its own augmented and virtual reality giants, just as how the domestic smartphone industry birthed global leaders like Huawei, Oppo and Xiaomi that rival Apple today.
Xu, now chief executive of Nreal, one of China’s highest-funded AR startups, is among a group of entrepreneurs uniquely positioned to build world-class hardware. The young generation is well-versed in both worlds, with work experience in Silicon Valley and often an Ivy League degree. They are also well-connected to capital and supply chains in China, which would support them through cycles of iteration to deliver powerful yet affordable products.
They might be proud of China’s technological progress, but they recognize supremacy doesn’t come overnight. More importantly, their firms often have intricate ties to the U.S., whether it’s for sourcing core parts or testing an early market.
Despite Beijing’s push for technological “self-reliance,” Chinese AR and VR companies still depend on imported chips like their smartphone counterparts. Because the industry is so young and no one really has a proven model for monetization, few investors and startups in China are willing to splurge on basic research.
But China has one important strength, said the founder of a Chinese AR startup who declined to be named: “In cutting-edge sectors, China has always lacked the talent to take things from ‘zero to one.’ However, China has the mass production and supply chain capabilities necessary for taking things from ‘one to n.’”
That was the case with smartphones. Once Apple demonstrated the technological and financial possibilities of handsets and gave rise to a production ecosystem around iPhones — in other words, catapulted the industry from zero to one — Chinese counterparts took cues from the American giant, made use of homegrown manufacturing resources and began delivering cheaper and even more powerful alternatives.
“I can’t imagine any Chinese corporations willing to invest in AR and VR as heavily as Microsoft, Apple or Facebook today,” said the founder, whose company sells headsets both in and outside China.
“On the contrary, China is good at playing catch-up by spending money on a race with a clear finish line. For example, chips. If there are already contestants in the area, so long as [Chinese firms] ramp up investment and follow the direction, they can deliver results.”
Chinese innovation
Although China, for the last decade, has been calling for more indigenous innovation, most of the advanced technologies found in AR and VR are still in the hands of foreign tech behemoths, several industry experts told TechCrunch. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chips are used almost exclusively by serious players, from Facebook’s Oculus Quest in the U.S. to Pico and Nreal in China. Advanced optical solutions, on the other hand, mainly come from Japanese and Taiwanese firms.

That’s not to say Chinese companies don’t innovate. Prominent venture capitalist and AI expert Kai-Fu Lee famously argued in his book “AI Superpowers” that while the U.S. has an edge in fundamental research, China is stronger on implementation and commercial application.
“It’s true that the more experimental efforts are happening in the U.S., though I’m not sure if any of those are mature already,” Tony Zhao, founder and chief executive of real-time video API provider Agora and a veteran from WebEx, told TechCrunch. “For Chinese companies, there are more opportunities in [user experience].”
As AR and VR come of age, Zhao’s company is devising a toolkit to let developers and organizations stream and record AR content from devices. Use cases by China’s educators have particularly impressed Zhao. One client, for example, built a tool allowing a teacher to interact with a student through a virtual store, where the two speak English while they respectively act as the cashier and the customer.
“I think it’s very revolutionary because a lot of kids are going to be very excited to learn from those kinds of tools. It’s more like a real experience and would be more natural for students to learn to use a language instead of just know the grammar,” said Zhao.
“These solutions are already creative, but also very practical.”
The Chinese market offers other aspects that can keep investors excited. As Gavin Newton-Tanzer, president of Sunrise International, Asia producer of the “mixed reality” (XR) conference AWE, pointed out to TechCrunch:
“Many like to say that in the U.S., Magic Leap sucked all the air out of the room. They raised tons of money and as a result, few wanted to fund [other smart glass startups]. It’d be like funding a competitor to Didi in China or funding a competitor to Uber in the U.S. … Few felt like anyone else could meaningfully compete.”
He reckoned the case is different on the other side of the globe. “In China, it doesn’t seem like that is happening. There’s diversity.”
Indeed, there’s still no clear leader in the fledgling industry in China, where startups like Hong Kong-based Mad Gaze, IDG Capital-backed Rokid and Xiaomi founder-backed Nreal compete fiercely in AR. There is a similarly tight race in VR among startups like DPVR, started by a former Intel engineer, and Pico Interactive, whose founder hailed from major VR OEM (original equipment manufacturer) Goertek, as well as tech incumbents like HTC Vive and Huawei.
“I think it’s really good for the industry,” Newton-Tanzer added. “More than anything else, I think local Chinese companies are doing a very good job in making [AR and VR products] cheaper.”
Market appetite
Though China still sees plentiful startups competing in AR and VR, the number getting funded has declined from the apex of the industry’s hype. In 2017, the Chinese AR and VR market saw 55 funding rounds and $264 million raised, according to data provided by research firm CB Insights. Year to date, there have only been 29 deals, which amount to $150 million in funding. Even prior to the pandemic that weakened the economy, the industry saw only 27 deals and $194 million raised in China during 2019.
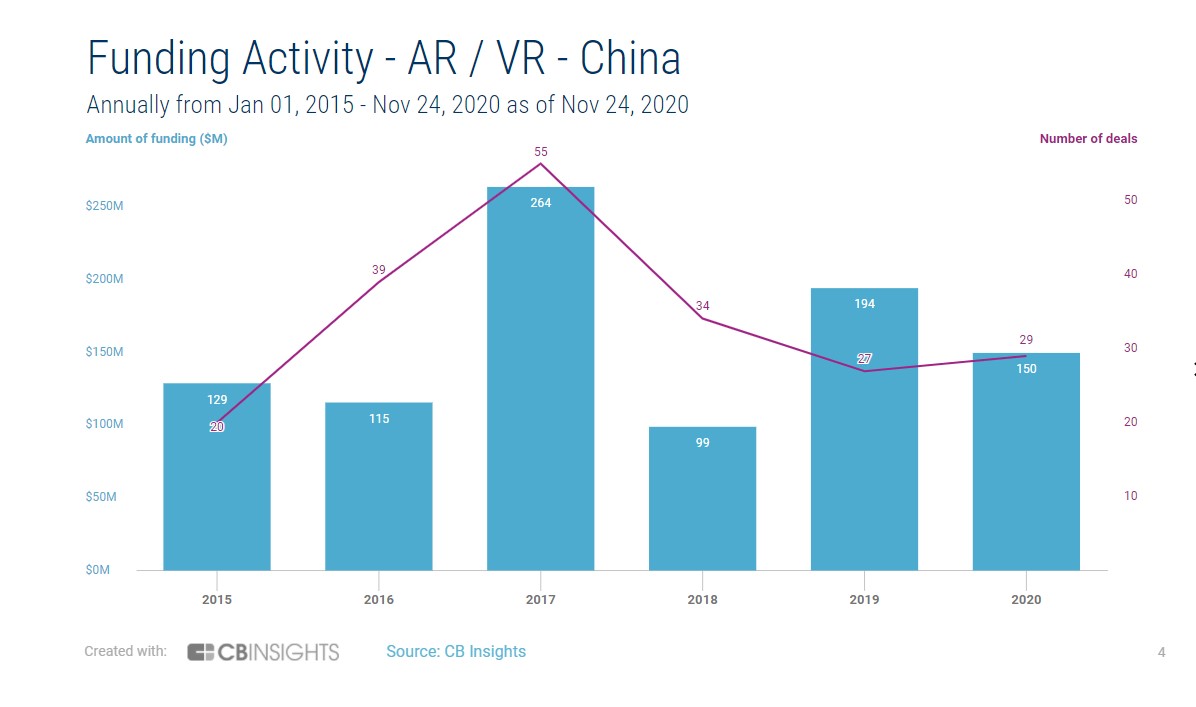
The waning enthusiasm in China mirrors that in the U.S., though American AR and VR startups are racking up more funding rounds and capital overall. Around the world, investors are questioning the viability of the emerging technology following the initial failure of Google Glass and Magic Leap’s dismal sales.
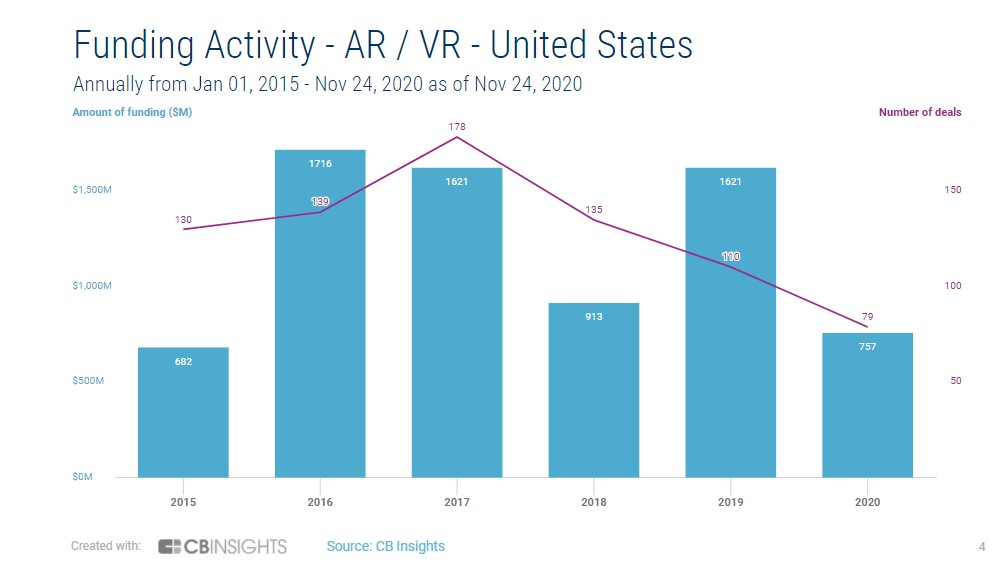
While fewer AR and VR companies are getting backed in China, Series B rounds have prevailed in recent times. It indicates that the remaining players have at least achieved certain milestones to keep investors interested in the nascent field, which is only shipping single-digit millions of units a year.
“There has been almost no success case in the industry yet, neither financially nor technologically. Startups need to keep raising money to spend on research,” said Seewan Toong, an AR/VR consultant. “Investors are more cautious these days. Many of the devices being sold at the moment are just for big corporations and government bureaus to do demos or are in niche markets like Oculus Quest.”
The majority of the advanced VR headsets were too expensive for the mass market until Facebook’s recent introduction of the more affordable Oculus Quest, which Toong says is “heavily subsidized and not profitable.”
“There is also no strong use case for the enterprise market as VR devices are still focusing on entertainment like Oculus,” he said.
AR has its own challenges. Though the emergence of mobile AR like Pokemon Go and AR-enabled shopping attracted early adopters, AR itself still has many technical challenges to overcome, from optical solutions and object tracking to virtual image overlay and costs, Toong said.
In more recent times, the advent of 5G has renewed investor excitement in AR and VR worldwide. The next-generation network technology enhances mobile broadband and, in turn, reduces latency and increases throughput for content to make more immersive user experiences. Data can also be processed at the edge, removing the need for expensive, high-end processors, thus reducing the price of the smart or AR glasses themselves, said Toong.
That’s why network operators have been eager to work with AR and VR device makers who can potentially help drive 5G adoption. Qualcomm, which touts a processor that lets headsets easily tether to 5G phones, has an initiative matching 15 top operators around the world to device makers, mostly Chinese ones like Oppo, iQiyi, Nreal, Shadow Creator and Pico.
Spurred in part by demand from the education sector and the introduction of more consumer-grade products, China’s AR shipments overtook the U.S. this year, IDC analyst Yexi Liao told TechCrunch.
Meanwhile, the U.S. remains the largest VR market in the world. As the prolonged pandemic continues to restrict people’s movement in America, many consumers are buying VR headsets for indoor entertainment and sports. In China, though, life and work have been back to normalcy since April, aside from small outbreaks that occasionally plagued some cities, so the idea of virtual entertainment is less appealing.
Tech war
As Huawei continues to feel the burn of U.S. sanctions, which cut off its core chip supplies and hobbled its smartphone business, one of the looming questions is whether the U.S. will restrict the export of AR and VR chips down the road.
Newton-Tanzer said he isn’t concerned, as the industry is a relatively “innocuous” one in comparison to smartphones.
“Unlike other industries, it’s not as sensitive as AI or drones, for instance. XR is mostly a visual-based technology enhancing how we experience the virtual world. It’s true for both VR and AR that the biggest use case is generally either entertainment or education. I actually think it’s an easier, happier conversation in an international environment.”
The industry is also so new that the U.S. won’t “post too much issue on this market yet,” said Liao of IDC. “It’s a bit different to smartphones where the U.S. is trying to fight for 5G domination. In terms of market size, [AR and VR] is nothing in comparison to the phone side.”

Conversely, foreign hardware firms may find it hard to sever ties with China, which remains a top destination for hardware manufacturing. Most of the world’s VR production is currently done in China, according to industry consultant Toong, while AR shipment is still scant.
In 2020, VR headsets are expected to account for over 83% of worldwide AR and VR shipments, reports IDC. That in part is due to the highly customized nature of AR’s use cases.
“There’s no easy software or operating system that works with [AR devices] yet and they have to be highly customized, so what you’re seeing is government bureaus buying 10,000 headsets … for a very specific use case,” said Newton-Tanzer.
The relatively small scale, in turn, makes it much easier to move AR production out of China if companies ever choose to.
“There’s not that much that would need to be moved. The lens technology, the technology behind SLAM, in general, the technology making AR glasses work, is so new and manufactured at such a small scale that many countries would make for a suitable manufacturing base,” Newton-Tanzer added. “However, in terms of building a scalable supply chain, I think for a long time, China will have natural advantages in manufacturing, and I doubt China is ever going to get cut out of production.”
Beyond China
It’s not uncommon these days to see Chinese hardware startups venturing beyond their home turf. Mad Gaze, for instance, is among the top five best-selling AR headset brands in the U.S., according to data from IDC. In VR, both DPVR and Pico rank among the top 10 players in America.
These companies not only come with products that are often on par with Silicon Valley but are able to offer lower prices thanks to China’s supply chain advantage and relatively cheap labor. As Nreal’s Xu told TechCrunch previously, “We are combining our technological know-how from overseas with great resources in China’s manufacturing industry.”
But going global is becoming trickier. Many Chinese companies are conflicted about their identity, sometimes downplaying their Chinese origin to avoid the regulatory scrutiny that has hit Huawei and TikTok in foreign markets. Those fixated on overseas push are aggressively working to localize, whether through hiring in the target country or getting over compliance hurdles. It will be interesting to see how Chinese AR and VR upstarts play their international expansion game.
7 investors discuss augmented reality and VR startup opportunities in 2020






























Comment