Every day, millions of people send pictures with Instagram and Snapchat filters to their friends, or catch a Pokémon on their screen as they walk down the street – casually using augmented reality in their lives. AR software and apps have reached most corners of the world thanks to the never-ending string of improvements in computer and mobile technology.
So far, Augmented Reality has been limited to entertainment, social media and highly specialised events; the best AR experiences can only be had with specialised glasses. However, as associated technology such as graphic processing power of devices and mobile networks improve exponentially, the mass adoption of AR is fast approaching. In fact, many predict that the use of AR glasses will become commonplace by 2023.
 Image Courtesy: Ali Pazani from Pexels
Image Courtesy: Ali Pazani from Pexels
With higher bandwidth and improved glasses, the very air in front of the user can become a part of the UI. Here is our take on the six ways in which AR will transform the future:
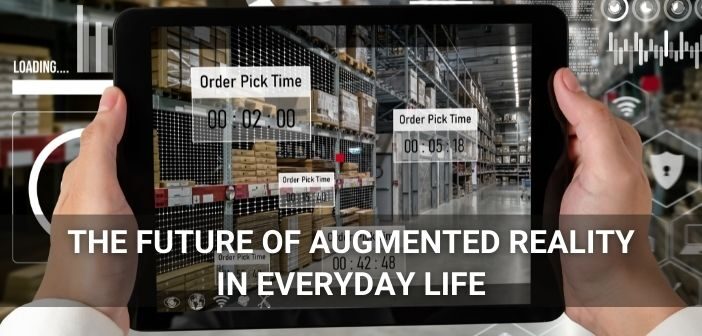
1. AR in Retail
The use of AR in mass retail is not a new concept; several large corporations have made forays into this domain for enhancing their customers’ retail experience. Presently, the most notable use case of AR in retail is Ikea’s furniture app Ikea Place, which lets users check out how a product might look in their house using a phone camera.
Currently, Ikea Place is only available on iOS, where it has garnered popularity for adding ease and comfort to the process of buying furniture. Retailers, especially eCommerce businesses, can take a leaf out of Ikea’s book and leverage the use of AR for instant simulation and testing of a product.
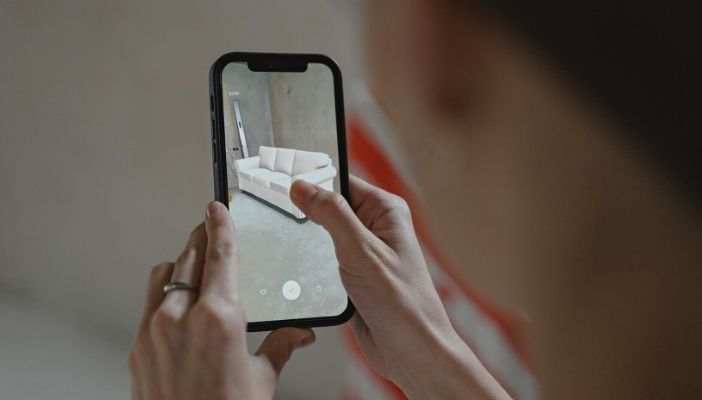 Image Courtesy: Tima Miroshnichenko from Pexels
Image Courtesy: Tima Miroshnichenko from Pexels
Particularly for industries such as fashion, accessories and decor – which rely on the customer’s subjective assessment – AR will bring about a paradigm shift in the purchase decision process. Other than making shop-from-home even more enticing and convenient, AR can be integrated within mortar stores to make them more attractive.
2. AR in Art
Art has adapted well to all advances in technology. There has been a rising demand for digital art by admirers and collectors across the world, the trending news about NFT art markets being a great testament to this demand. Adobe, the creative software giant, has launched Adobe Aero and XR creation packs for artists looking to use augmented reality as the new medium of creativity.
By using AR, artists will have the freedom to draw in 3D, pin their artwork to any corner of the world, and share it – all without obstructing or replacing anything in ground reality. The consumers of art can be a part of this ‘free-world’ exploration as well: using their AR goggles, they can choose to engage with a ‘themed’ world, by altering or enhancing the perception of the physical elements around them. They can also opt to imbue their interface with graphic elements designed by their favourite AR artists – for example, a custom-tinted sky. The possibilities are limitless.
3. AR in Gaming
The AR video gaming industry is estimated to reach USD$ 28.8 billion by 2026. Apart from their novelty factor, AR games are especially entertaining as they alter the way we perceive and interact with our physical environments. The mobile game Pokémon Go was wildly famous for a long while thanks to this AR interface, as people were deliberately going out and exploring their surroundings in order to catch their favourite critters.
 Image Courtesy: Anton from Pexels
Image Courtesy: Anton from Pexels
With the easier availability of AR goggles, mobile-based games will be left in the dust. The upkeep generation of AR Goggles come with 6DoF and relative spatial positioning, which enables devices to track a user’s movement in all directions and determine their direction of motion. This opens up many possibilities for developers to create adrenaline-pumping games.
4. AR in Cars
AR is well suited to the task of optimising information display to streamline user experience. Every aspect of car manufacturing, retail, and even usage can benefit from this capability.
At the industrial production end, AR can enhance worker productivity by providing them with a constant visual aid to regulate the quality and accuracy of each task. For automobile designers too, AR can prove to be a handy visualization tool. At the user’s end, AR can aggregate and display precise on-road data – measuring the user’s distance from other cars on the road, relative speed, and navigation cues for the best available route.
Many industry giants like Mercedes-Benz and Hyundai have jump-started the transition by introducing AR-enhanced HUDs and owner manuals. As innovations continue, it won’t be long before most cars on the road are fitted with windshields that double as AR interfaces.
5. AR in Education
Augmented Reality is not only meant for streamlining information – it can also enable a richer visualisation experience for complex data. The field of education can benefit greatly from this capability, bringing the whole world inside a classroom with nothing but an app and a headset.
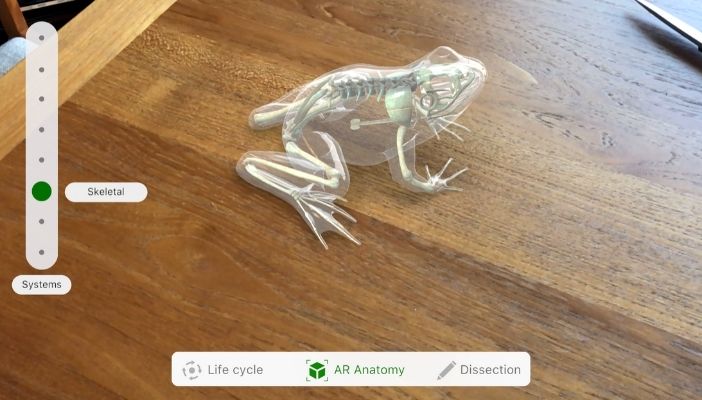 Image Courtesy: Froggipedia
Image Courtesy: Froggipedia
A small but significant example of this is the Froggipedia app, available to Apple iPad users. The app replaces the dissection module from school labs by providing a vivid virtual rendering of a frog that users can explore in AR. While VR has been incorporated in the classroom with far greater ease, AR can be particularly useful for self-guided studies and topical deep-dives – bringing a level of detail to the classroom that may not otherwise be possible.
With AR, students can learn in a hands-on capacity, absorbing information faster and more effectively. Bringing ARVR into the classroom is also the surest way to accelerate the adoption of these technologies.
6. AR in Medicine
Medicine is a precise science where a single misstep can have fatal consequences. In surgery, especially, data and dexterity play an equal part in ensuring a procedure’s success. AR can help save lives by providing surgeons with an overlay of vital information and procedural checkpoints; additionally, it can streamline the data feed for vital signs, making it easier for surgeons to focus on the task at hand.
Microsoft has made the leap with the Imperial College of London by employing the Hololens in a tissue reconstruction surgery. While highly specialized diagnostics are available, none of them currently use AR holographic technology to project procedural guides. By minimizing the information and workflow gap, AR is set to play a big part in reducing the risks and margins of error associated with surgery.
The ARVR market is exploding with promise, estimated to reach $ 766 billion by 2025. Of the current market share, investment in AR exceeds VR – a good indicator of how much trust the technology has earned for its potential to change our lives. While the future and scope of Augmented Reality are yet to unfold completely, we can be sure to witness an explosive change in the way we lead our lives in the near future.